为了保证产品质量,制药业必须使用专用于设备消毒和保护的清洁剂。 虽然我们日常生活中使用的清洁产品多种多样,但制药公司为保证产品质量必须使用专用清洁剂,如非离子洗涤剂。
Different Types Of Parenteral Preparations
Parenteral preparations are sterile pharmaceutical products administered to the human body by injection. Only liquids can be injected which means that the pharmaceutical parenteral preparation must either be a liquid which can itself be injected safely, or it may be a material that can be diluted with sterile water (commonly referred to as ‘water for injection’) or other sterile solvent before it is administered. Liquids other than water must not interfere with the stability and efficacy of the preparation. Some substances may be added to increase the stability and efficacy of the preparation, but it is important that such additives do not cause adverse effects or toxicity. Coloring agents are not permitted in parenteral preparations.
If parenteral preparations are to be stored in multiple dose containers, antimicrobial preservatives may be added to the formulations, which prevents and inhibits the growth of microbes in the container. It is necessary to validate the effectiveness of such preservatives before the start of the parenteral production process. Also, if the active ingredient(s) have the potential to oxidize and degrade, manufacturers can add anti-oxidants to the parenteral preparation, or the air in the container in which it is to be stored may be eliminated by evacuation, or displaced with nitrogen or other inert gas.
Containers
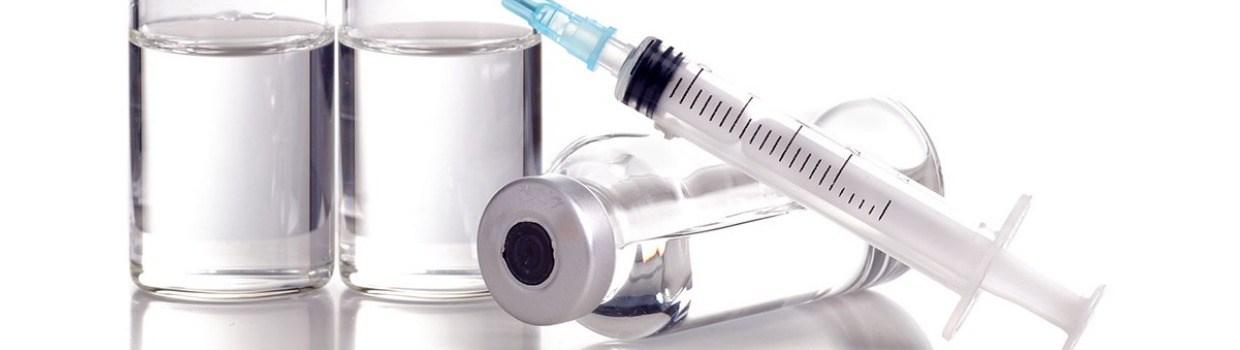
Parenteral preparations may be supplied and stored in a variety of containers, including vials, bottles ampoules and, for large quantities of liquids, bags. All of these containers must be transparent to allow for visual inspection of the content. The container must not contain any materials that may adversely affect the quality of the product during the handling, storage and use. Traditionally glass has been preferred for containers that store parenteral products, especially borosilicate glass which is more resistant to chemical attack than low cost soda lime glass. Plastics are now becoming more common, however, and several types are in common use. The choice of material is governed by the composition of the parenteral product and standards governing the choice of materials are set by the National pharmacopeias, for example the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention (USP), The Japanese Pharmacopoeia (JP), and The European Pharmacopoeia of the Council of Europe (EP). These institutions set quality standards for active pharmaceutical ingredients, drug products, excipients, packaging materials, labelling and storage conditions,
Closure/Sealing
In the case of bottles from which injectable samples are to be withdrawn, a special type of closure is required. These must prevent any microorganism or bacteria from entering, The closure material must be made of compatible material that will allow a hypodermic needle to pass through with minimal disruption or shedding of material and at also has the ability to reseal itself once the needle is removed. Elastomers are widely used as closure materials for bottles. They are also used in other primary parenteral packaging as stoppers for vials, plungers and tip caps for pre-fillable syringes, plungers and seals for cartridges and ports for plastic bags.
Inspection/Quality Control
To ensure the high quality, according to the Good Manufacturing Process, is maintained for parenteral product containers, each final container must be individually inspected for any contaminants. Contaminated containers must be rejected and removed.
Labelling
Parenteral products labels must include the name of the preparation, active ingredient amount, storage condition and the diluent or solvent required to achieve the desired concentration for the product to be administered. The label should not cover the whole bottle so that the product can easily be inspected.
Parenteral Preparation Types
- Injection. Injections contain sterile solutions and are prepared by dissolving the active ingredient and other substances in Water for Injection or other suitable non-aqueous base or a mixture of both. The solution to be injected may show sediments which can be dispersed easily by shaking the container. The suspension should remain stable in order to deliver a homogenous dose whenever withdrawal is made from the container.
- Infusions. These parenteral preparations are composed of sterile aqueous solution with water as its continuous phase. The preparations are free from bacterial endotoxins or pyrogens and are turned isotonic with blood. They do not contain any antimicrobial preservatives.
- Powder for Injection. These are sterile solid compounds that are distributed in their final volume when the vial or container is shaken to form a clear particle-free solution.
- Concentrated Solutions for Injections. The concentrated solutions are diluted with water for injection before they are administered through injection or through intravenous infusion.
- Implants. These solid sterile preparations are implanted in the tissue in order to release the active ingredient for long periods. They are stored in sterile containers individually.